Non Polar Amino Acids
Of the polar amino acids asparagine glutamine serine threonine and tyrosine are neutral. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms the nine amino acids humans cannot synthesize are phenylalanine valine threonine tryptophan methionine leucine.

Notes On Amino Acids An Introduction Biology Exams 4 U Chemistry Lessons Amino Acids Biochemistry
An amino acid that can be made by humans and so is essential to the human diet.

. Aliphatic Amino Acids. Acidic and polar 4. On the basis of polarity amino acids are categorized into 4 groups.
Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional. Typically only 2-3 essential. The nonessential amino acids.
Amino Acid can be classified based on their structure and the structure of their side chains ie. The amino acids have not been tested pregnancy and breastfeeding but a free form amino acid blend that does contain tryptophan can be used. The most frequent active site amino acid residues out of the 20 amino acids forming the protein are polar amino acids aspartate cysteine glutamate histidine Serine and lysine.
Mnemonic to memorize Polar AA with a neutral R group. Cofactors are non-proteinous substances that associate with enzymes. Non-polar amino acids can be further split into alkyl or aromatic while the polar amino acids can be split into neutral acid or basic.
Aspartate and glutamate are acidic amino acids. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Basic and polar For example side chains having pure hydrocarbon alkyl or aromatic groups are considered non-polar and these amino acids are comprised of Phenylalanine Glycine Valine Leucine Alanine Isoleucine Proline Methionine and Tryptophan.
Non essential amino acids. Although glycine has so few carbon atoms it is neither hydrophilic nor hydrophobic. All AAPPTec Fmoc amino acids are 99 pure for optimum peptide synthesis yields.
Aliphatic amino acids are non-polar and hydrophobic. These are also known as Hydrophobic. Amino acids have high melting point 200-300 o C due to ionic property.
The ranking of polarity will depend on the relative ranking of polarity for various functional groups as determined in functional groupsIn addition the number of carbon-hydrogens in the alkane or aromatic. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. These amino acids are polar and possess neutral pH value.
Classification of Amino Acids. Now two basic subcategories are. If individual amino acids are used when breastfeeding with approval from the doctor moms nurse and then use the amino acid and dont nurse for the next 4 hours always watching for adverse effects in baby.
Amino acids are insoluble. An essential amino acid or indispensable amino acid is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand and must therefore come from the diet. The majority of amino acids both polar and non-polar are in fact neutral.
Side chains which have various functional groups such as acids amides alcohols and amines will impart a more polar character to the amino acid. As the numbers of carbon atoms on the side chain increases hydrophobicity increases. The R group can be either of Alkyl groups with an alkyl chain or Aromatic groups.
1 Non-Polar Amino Acids. Valine substitution for glutamic acid in hemoglobin results in. Solubility of amino acids depends upon polarity iso-electric point nature of solvent pH and temperature.
Amino acids are soluble in water and ethanol ie. Polar Amino Acids Mnemonic. If the side chain contains an extra element of carbolic acid the amino acid becomes acidic.
A cofactor is essential for the functioning of an enzyme. The following video goes into more detail about the various chemical properties that help to classify different amino acid groups. Polar solvent and insoluble in non-polar solvent like benzene ether etc.
The aliphatic amino acids are alanine glycine isoleucine leucine proline and valine. The nonpolar amino acids are as follows with more information on each. Tyrosine is moderately hydrophobic and contributes strongly to β-sheet formation.
Valine is a non-polar highly hydrophobic residue that strongly participates in β-sheet formation. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature by far the most prevalent are the alpha-amino acids which comprise proteins. Glycine Serine Threonine Cysteine Tyrosine Glutamine Asparagine.
Polar with neutral R group Hydrophilic STY Serine Threonine Tyrosine CNQ Cysteine Aspargine Glutamine. The nonpolar amino acids have R groups mostly made up of hydrocarbons though the amino acids methionine and cysteine also each feature a sulphur atom.

Pka Amino Acids Table Study Tips College Amino Acids Amino Acids Biochemistry Study Guides

Amino Acids Chemistry Biochemistry Chemistry Basics
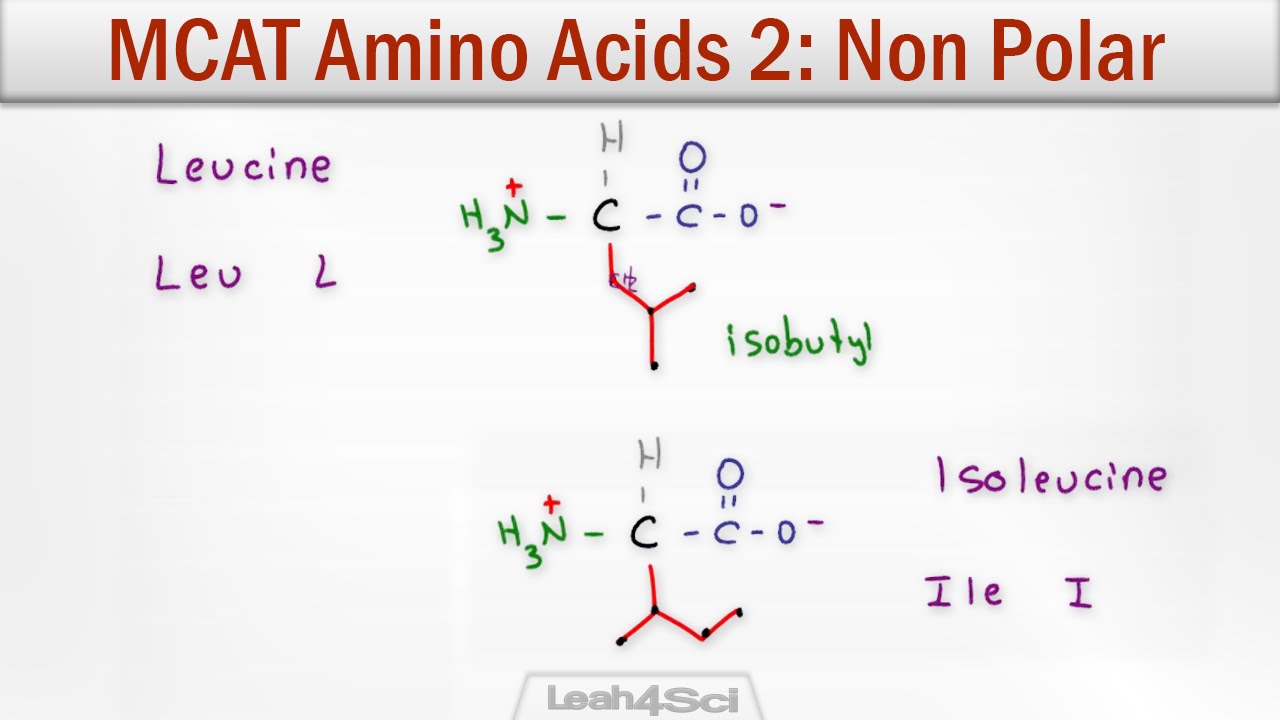
Mcat Amino Acids 2 Hydrophobic Side Chain Structure And Characteristics Mcat Chemistry Organic Chemistry

20 Different Amino Acids Structure To It Twenty Different Types Of Side Chains 20 Amino Acids Study Chemistry Biochemistry Chemistry
No comments for "Non Polar Amino Acids"
Post a Comment